近日,广东省科学院中乌焊接研究所智能化搅拌摩擦焊接与制造团队在铝-铜异种金属搅拌摩擦焊接技术研究方面取得新突破。相关研究相继发表于《材料科学与工程》和《材料加工技术》杂志。
铝-铜复合结构散热器是保障新能源汽车动力电池安全服役并提升其使用寿命的关键部件。但铝、铜由于物理、化学性能差异较大,焊接制造过程中极易产生缺陷,急需突破此技术瓶颈。该团队创新性地采用静轴肩搅拌摩擦焊接(SSFSW)新方法实现了铝-铜异种金属高质量的焊接,接头抗拉强度可达243MPa。研究发现,采用非旋转轴肩可抑制材料混合,避免由于铝、铜物理性能差异导致的裂纹、孔洞等缺陷。同时,该方法可以显著降低焊接温度,有效抑制界面金属间化合物的生成,降低了接头脆性。
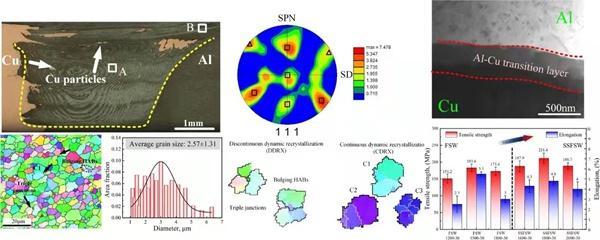
此外,团队通过对SSFSW过程中的剪切应力的计算,揭示了接头搅拌区织构形成的新机制。
该研究工作得到国家重点领域研发计划项目、国家自然科学基金项目和广州市对外科技合作项目的支持。
相关论文信息:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2022.142754 https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2021.117402
(文:朱汉斌)
Abstract
The fundamental reasons for the poor mechanical properties of the Al–Cu conventional friction stir welding (CFSW) joints are serious material mixing and excessively thick intermetallic compounds (IMCs). In this study, stationary shoulder friction stir welding (SSFSW) was innovatively applied to join the Al–Cu dissimilar materials. The results indicated that the material mixing and the IMCs growth were successfully suppressed. Compared with the CFSW, the grains in the SZ of the SSFSW joint were refined and the plastic deformation in the SZ was enhanced. This was attributed to the frictional driving force of SSFSW was higher than that of CFSW. The mutual diffusion reaction of Al and Cu elements was inhibited owing to the lower heat input of the SSFSW. The mechanical properties of the joints were significantly improved by the SSFSW. The tensile strength of the optimal SSFSW joint was found to be 211.4 MPa which is 15.1% higher than that of the optimal CFSW joint. Moreover, the fracture occurred in the Al matrix. Reducing the stress concentration in the SZ caused by materials mixing was shown to be the main mechanism for SSFSW to improve the tensile performance of the joint.